TB (Tuberculosis)
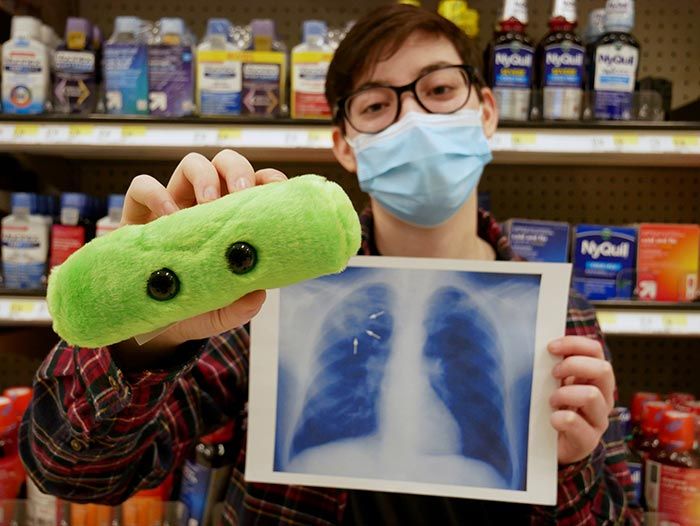
This plush representation of TB provides a memorable hands-on-way to learn about this global disease and how it targets the lungs and throat. While TB has infected humans for millennia, it remains a disease of the present with 11 million cases per year.
Unique gift for educators, family, friends, doctors, scientists, public health experts and world travelers. Features high quality materials and educational card with fascinating facts about this microbe and how it spreads.
GIANTmicrobes TB is soft, cuddly and is a unique gift and learning tool for loved ones and friends interested in global health.
Size: 15 x 6 x 6cm
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 40-60cm XL (XL) 25-38cm Original (PD) 12-20cm Minis (MM) 5-10cm each Keychain (KC) 5-10cm with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about TB (Tuberculosis)
FACTS: Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by the mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. TB can infect any part of the body, but typically targets the lungs and throat. Coughing or sneezing by infected persons is the most common cause of transmission. Unfortunately, TB bacteria can remain in a latent state so that infected persons who do not initially contract TB are still at risk of developing the disease later in life, should their immune systems ever weaken. (During the latency period, the TB-resistant host shows no symptoms of TB and is not contagious.)
While TB has been a human scourge since ancient times, it remains a disease of the present. According to USAID in 2023, there are 11 million cases and 1.6 million deaths caused by TB each year.
Although TB symptoms vary depending on which part of the body the disease infects, symptoms of TB of the lungs typically include:
• A bad cough lasting more than two weeks
• Coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep in the lungs)
• Chest pain, fever, fatigue/weakness, chills, weight loss, loss of appetite, and night sweats
Both active and latent TB can be detected by injecting tuberculin under the skin and examining resultant bumps. Testing is recommended for:
• Persons who have symptoms of TB, or have been exposed to TB
• Persons from places with elevated TB rates, such as Africa, Asia, the Caribbean, Eastern Europe, and Latin America – as well as prisons, migrant farm camps, nursing homes, and homeless shelters
• Persons with weakened immune systems, such as H.I.V. carriers, children, and the elderly
Fortunately, drug treatments are available for TB. However, to prevent TB bacteria from becoming drug-resistant, patients must not stop drug treatments prematurely. While the symptoms of TB may abate after a few weeks, the bacteria are not fully eradicated for at least six months.
Information is provided by the Center for Disease Control.
| Name | Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the species of bacterium that causes the TB disease. The name White Plague comes from the paleness of people with TB. |
|---|
| Where It Lives | People are infected by breathing in airborne TB bacteria. TB disease is caused when the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from multiplying in the body. Therefore, people with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing the disease. Sometimes, people can be infected without being contagious or becoming sick. This condition is called latent TB infection. Fun gift for doctors or historians! |
|---|
| Symptoms | The bacteria attack the lungs, which can cause coughing and chest pain. Other symptoms include chills, fever, night sweats, weakness, and loss of appetite. |
|---|
| Cure | There is a vaccine. People with latent TB infection should take drugs to prevent the disease. People with TB disease should take 6-9 months worth of antimycobacterial drugs like isoniazid. Without treatment, the disease can progress and become fatal. |
|---|
| History |
1882: Robert Koch discovered the bacterium that causes TB- Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 1921: The BCG vaccine for TB, developed by Calmette and Guerin, was introduced. 1952: Selman Waksman awarded Nobel Prize for methods leading to the discovery of streptomycin, the first drug to treat TB. Albert Schatz and Elizabeth Bugie were also part of the research team. Big Outbreaks: 1700-1900: The White Plague in Europe caused millions of deaths. 1992: TB in the United States peaked for the decade with >26,600 cases for the year. Recent Outbreaks: March 2015: 27 people at a Kansas High School have TB. In 2022, the largest number of new TB cases occurred in WHO’s South-East Asian Region (46%), followed by the African Region (23%) and the Western Pacific (18%). Around 87% of new TB cases occurred in the 30 high TB burden countries, with more than two-thirds of the global total in Bangladesh, China, Democratic Republic of the Congo, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan and the Philippines. |
|---|
| Fascinating Facts |
TB was one of the leading causes of death in the U.S. in the early 1900’s. Famous People Who Had TB: Eleanor Roosevelt died of a drug resistant strain of TB. |
|---|