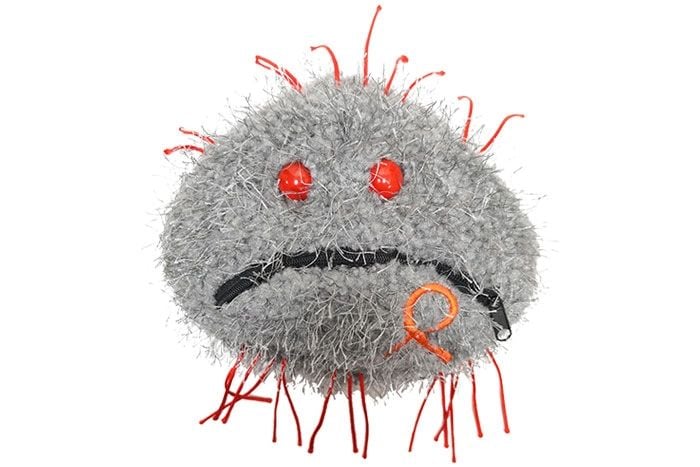
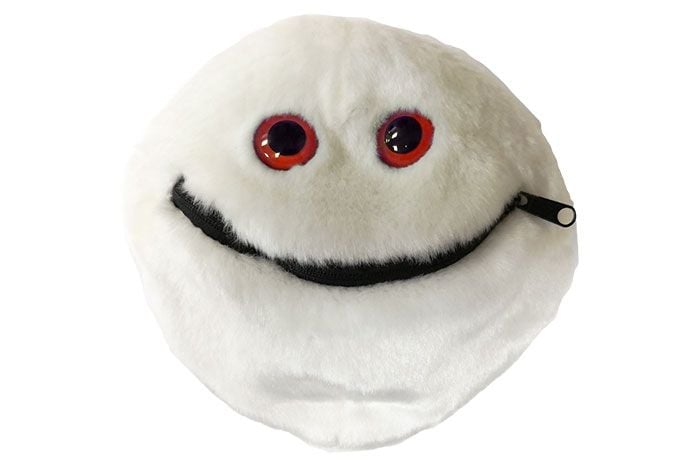
Leukemia (Malignant neoplasm)
Out of Stock
Our Cancer cell can be "cured" by flipping it inside-out!
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 40-60cm XL (XL) 25-38cm Original (PD) 12-20cm Minis (MM) 5-10cm each Keychain (KC) 5-10cm with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Leukemia (Malignant neoplasm)
FACTS: The term cancer applies to more than 100 different diseases, all of which have two things in common. As a result of genetic damage, normal cells become cancerous and can grow in an uncontrolled manner. In addition, these cells are able to invade other tissues, disrupting and destroying the structures and organs that they infiltrate.
As with most cancers, leukemia develops due to genetics as well as risk factors including poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and lack of exercise. Although the fundamentals of treatment – surgery, radiation and chemotherapy – have not changed in many years, advances in imaging, diagnosis, and sophisticated methods for delivering therapies have greatly improved their effectiveness. In addition, breakthroughs in immunotherapy are now being put into practice. As a result, many who develop cancer have a greatly improved chance of recovery compared to a few decades ago.
Leukemia is cancer of the bone marrow, the lymphatic system and other blood-forming tissues. This disease involves the abnormal production of white blood cells, which may not function properly to fight infections.
There are many types of leukemia, classified by the speed of progression and the type of white blood cells involved – namely lymphoid cells or myeloid cells. Acute types of leukemia impact immature blood cells and are fast spreading. Chronic types involve more mature blood cells and these cancers develop more slowly. Some forms are more common in adults while others are found mostly in children, such as acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Leukemia symptoms are often vague and easy to overlook since they resemble other common illnesses. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, frequent infections, weight loss, swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver or spleen, bruising, easy bleeding, red spots on the skin, excessive sweating and bone pain.